Upcoming Events
Stay up to date with the latest space events.
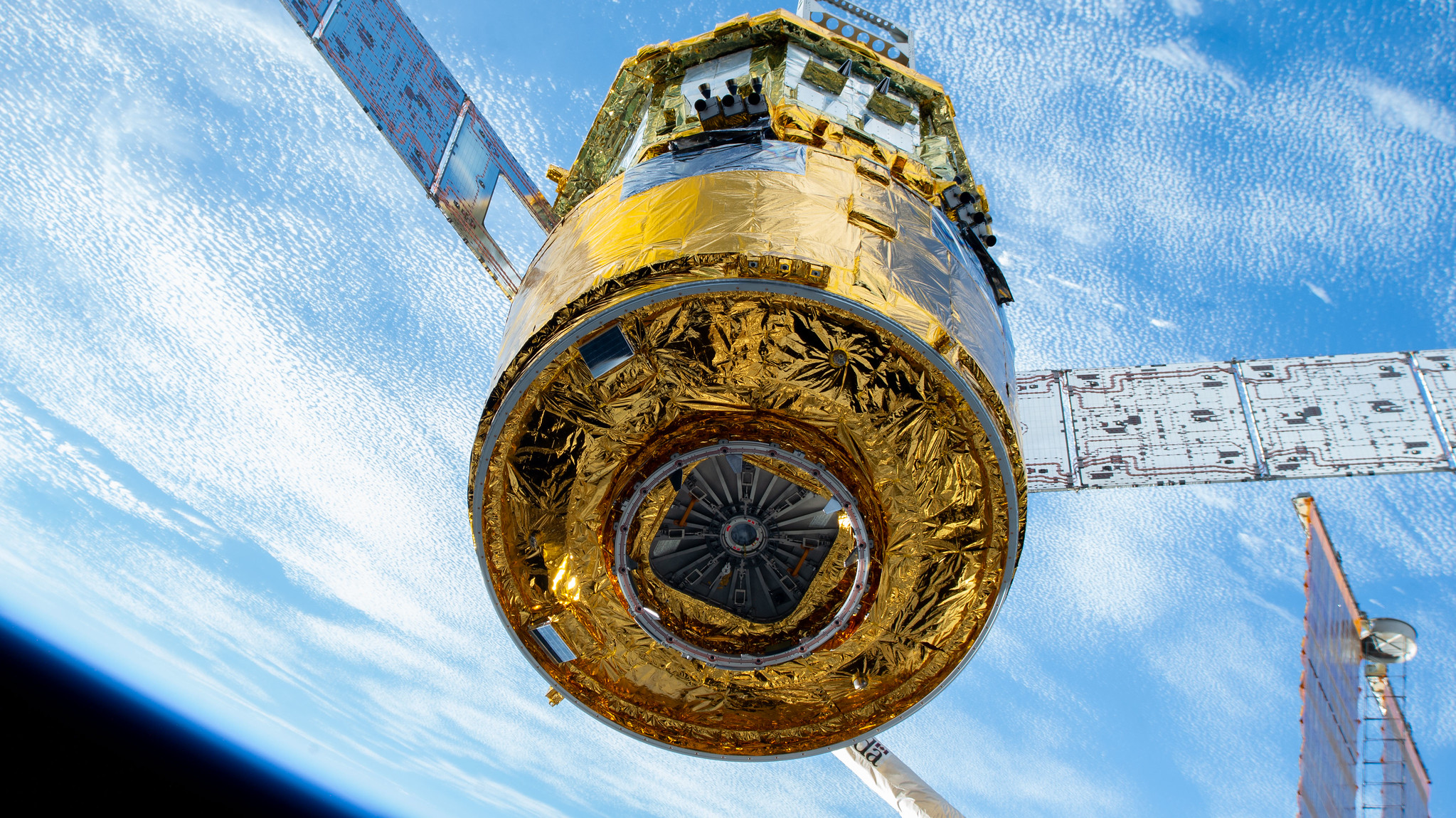
HTV-X1 Release & Reentry
The JAXA HTV-X1 will be unberthed from the ISS before initiating a destructive reentry into the Earth's atmosphere taking waste along with it.

HTV-X1 Release & Reentry
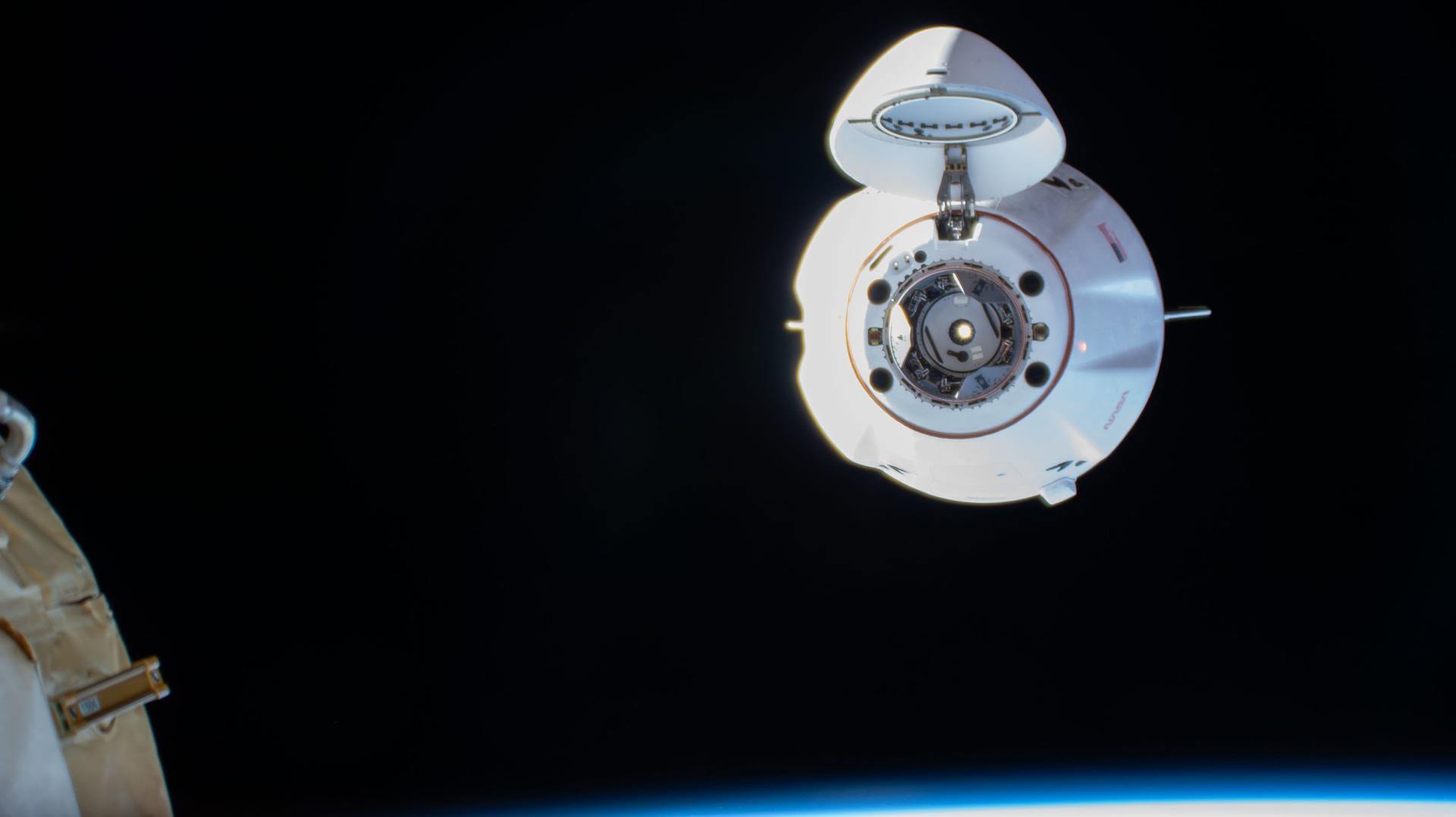

SpaceX CRS-33 Dragon Undocking
The SpaceX CRS-33 Dragon spacecraft will undock from the International Space Station ahead of its reentry, splashdown and recovery.
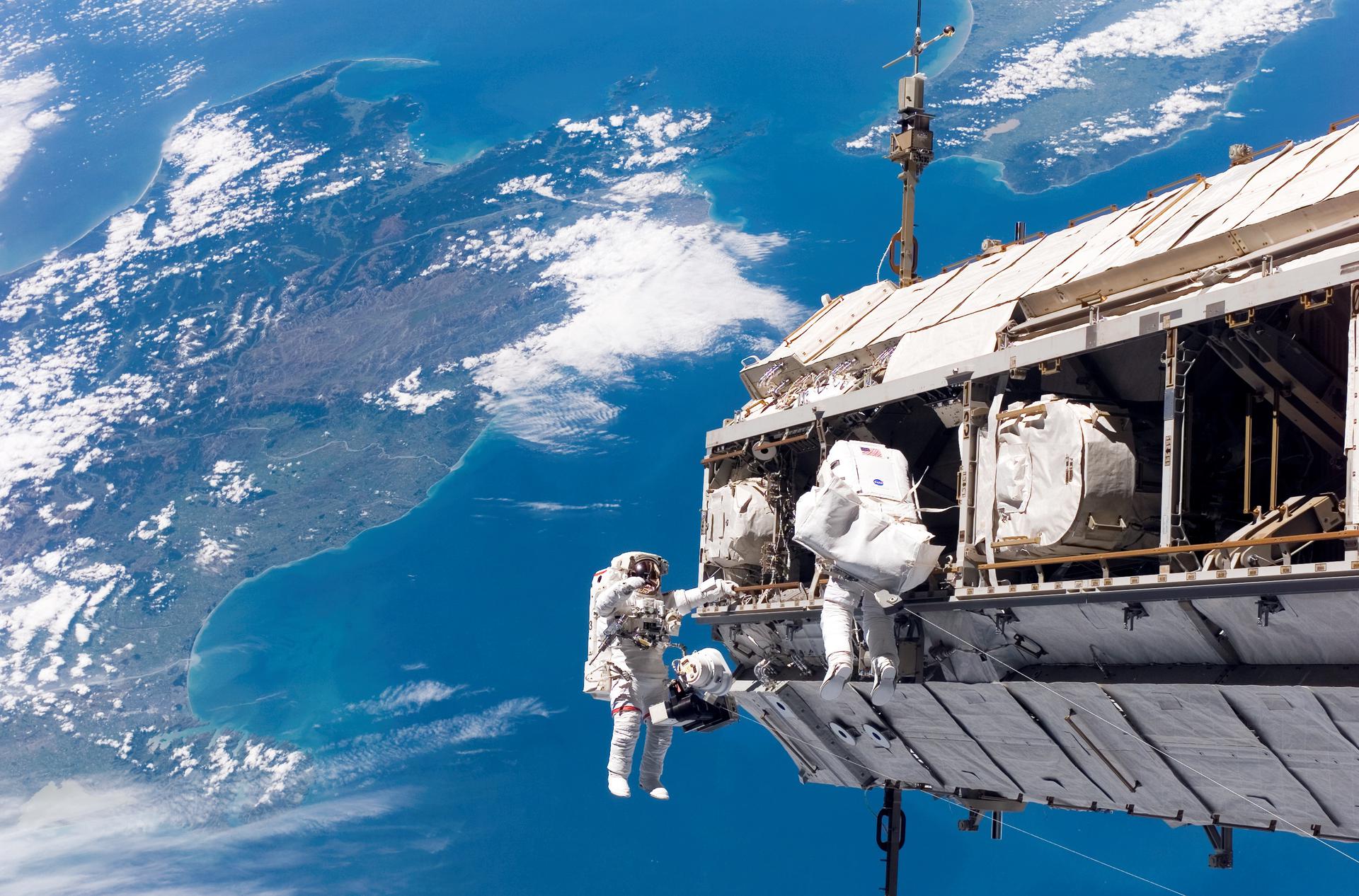

US EVA-95
Two astronauts will replace a high-definition camera on camera port 3, install a new navigational aid for visiting spacecraft, called a planar reflector, on the Harmony module’s forward port, and relocate an early ammonia servicer jumper — a flexible hose assembly that connects parts of a fluid system — along with other jumpers on the station’s S6 and S4 truss.

US EVA-94
Two astronauts will exit the station’s Quest airlock to prepare the 2A power channel for future installation of International Space Station Roll-Out Solar Arrays. Once installed, the array will provide additional power for the orbital laboratory, including critical support of its safe and controlled deorbit.

Hayabusa2 S-Type Asteroid (98943) Torifune Flyby
As part of its mission extension, JAXA's Hayabusa2 spacecraft will observe S-type asteroid (98943) Torifune during a high-speed fly-by.
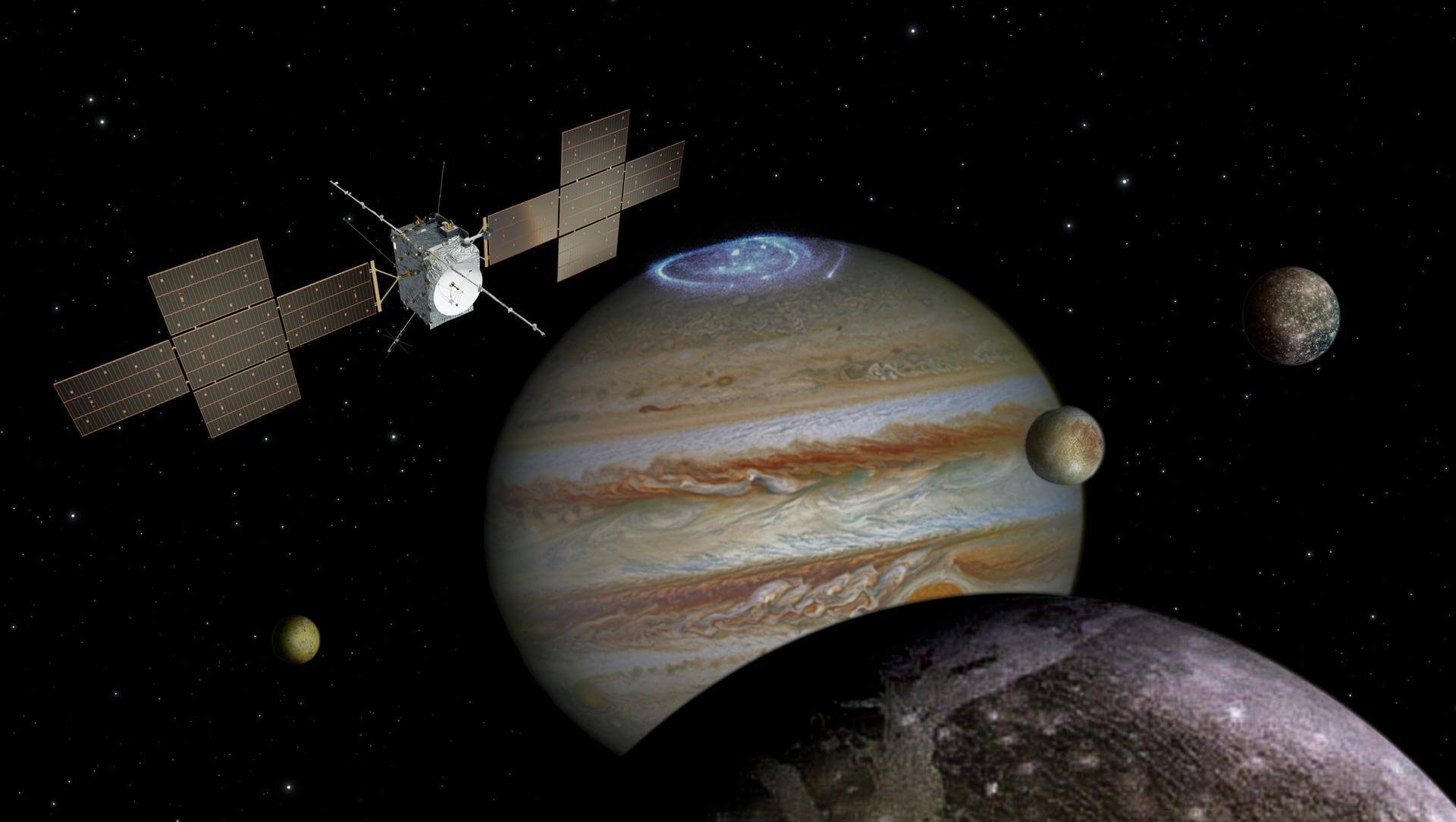

Juice Earth Flyby
Third flyby of ESA's Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (Juice) mission on its way to the Jovian system.
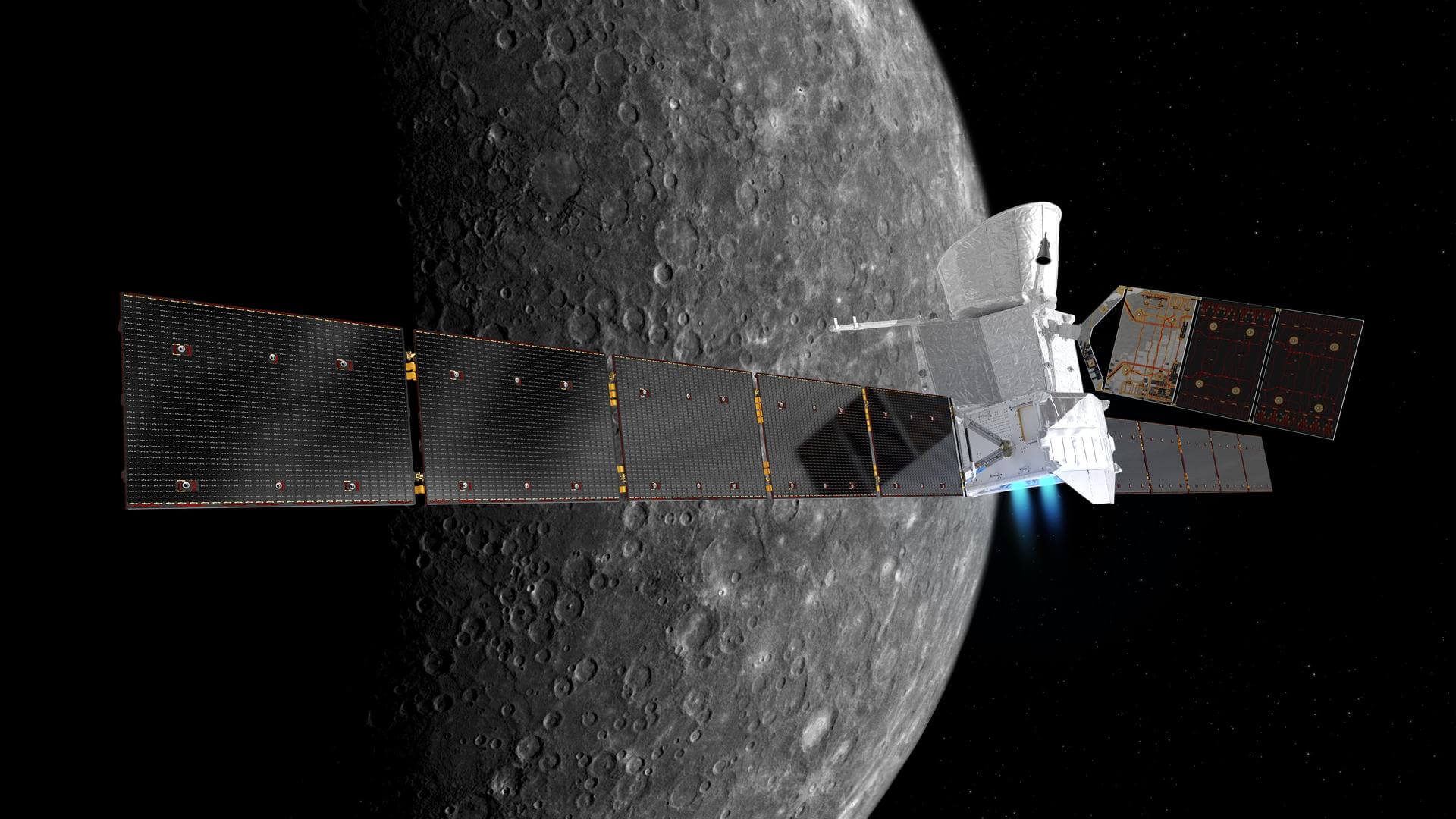

BepiColombo Mercury Orbit Insertion
Orbital insertion around Mercury of the ESA-JAXA BepiColombo mission.
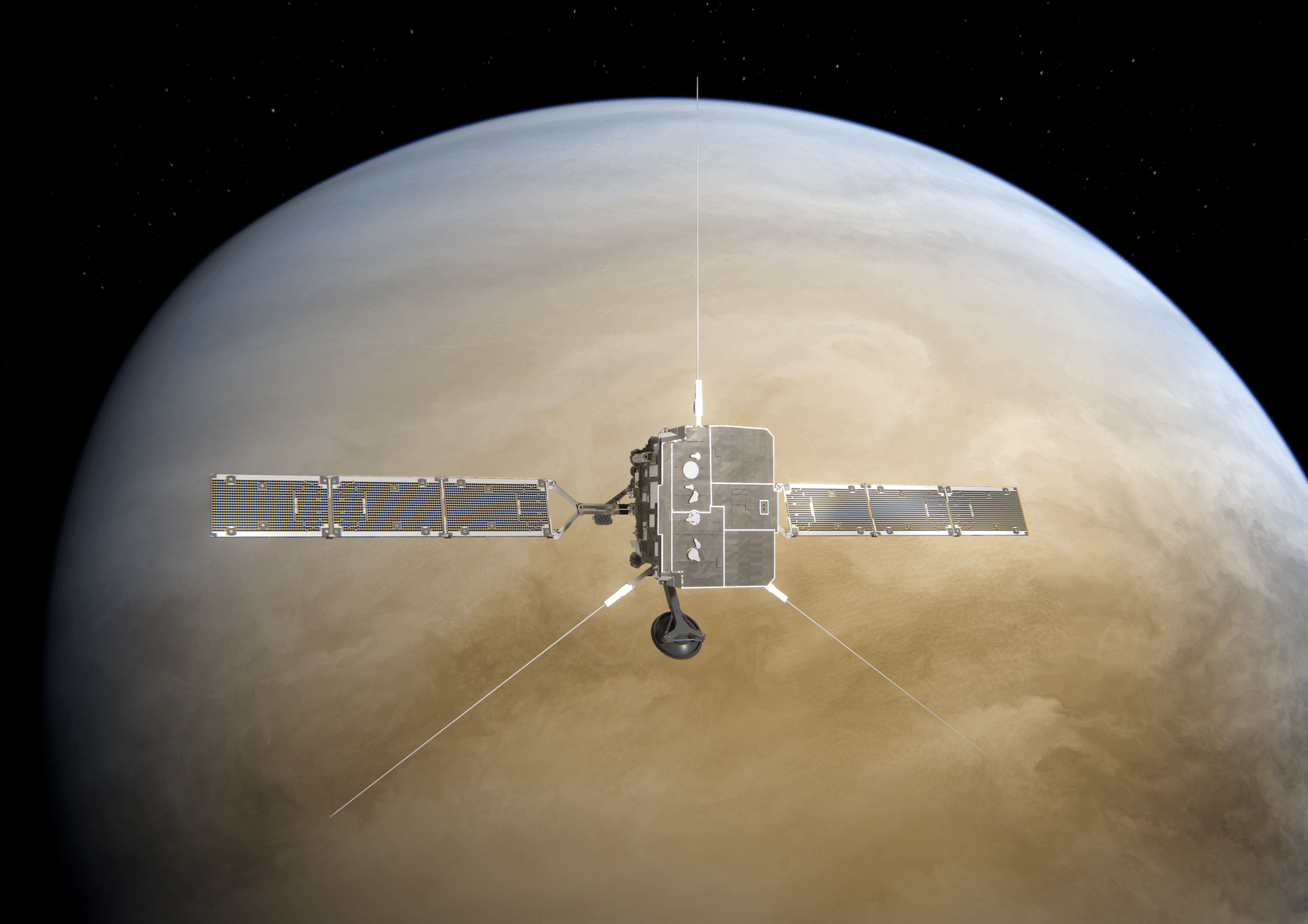
Solar Orbiter Venus Flyby
Solar Orbiter, a partnership between ESA and NASA, will perform a gravity assist maneuver with Venus on December 24, 2026. Throughout its mission it also makes repeated gravity assist flybys of Venus to get closer to the Sun, and to change its orbital inclination, boosting it out of the ecliptic plane, to get the best – and first – views of the Sun’s poles.
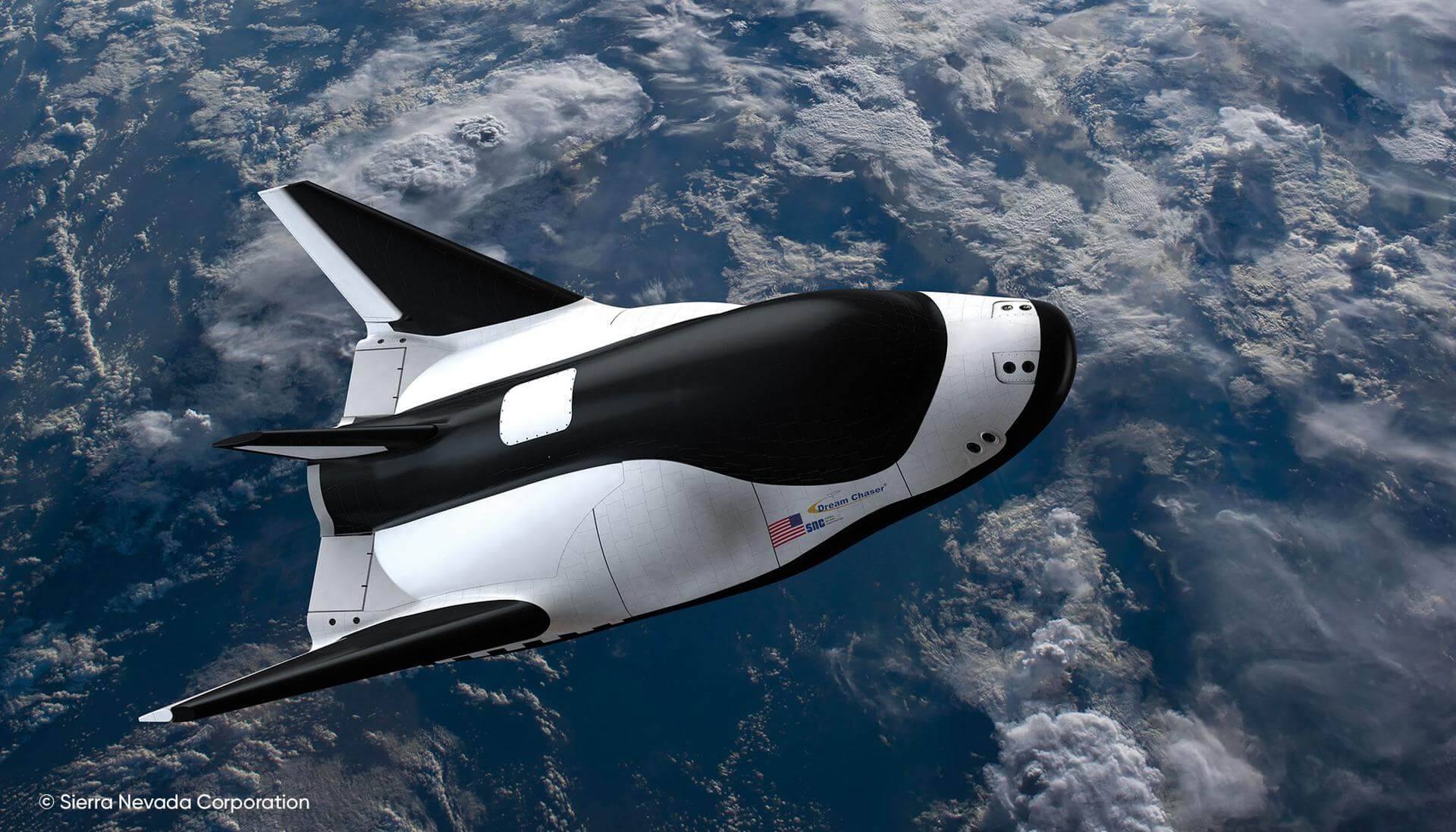

SNC-1 Dream Chaser Berthing
NASA TV will livestream the rendezvous and capture of Sierra Nevada Corporation's Dream Chaser cargo craft to the International Space Station.
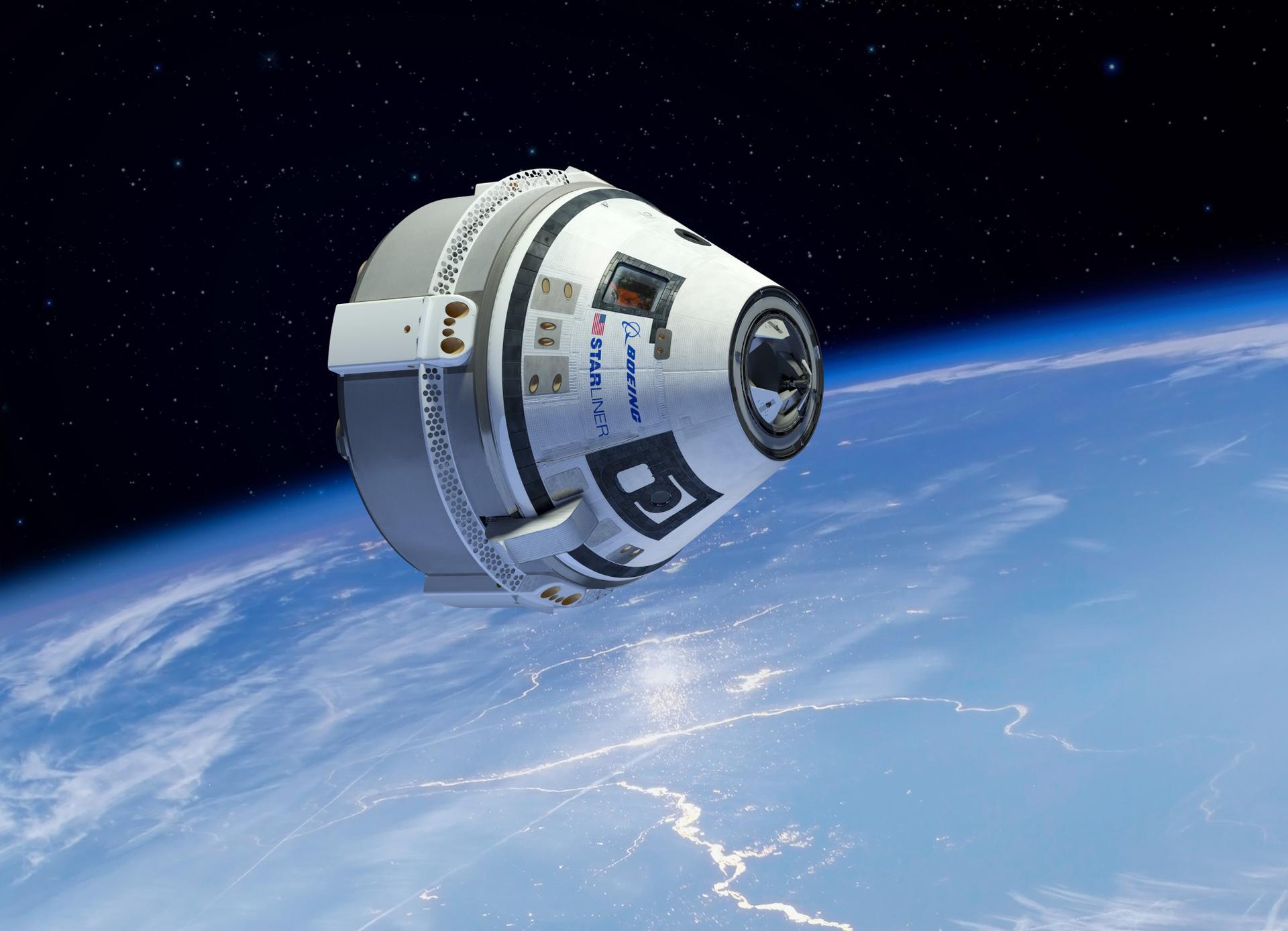

Boeing Starliner-1 Undocking
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner will undock from the International Space Station and conduct a deorbit burn as part of its first operational mission. Following the deorbit burn the capsule will renter the Earth's atmosphere and land at the 'White Sands Missile Range' using its parachutes.